
Using the converter is easy. Just enter a CIDR value like this: 192.168.1.0/24.
The first part is the IP address, and the number after the slash tells how many bits are used for the network.
Once you have entered it, click ‘Convert’, you will instantly see the full IP range.
Why Convert CIDR to IP Range?
Converting CIDR to an IP range makes it easier to understand and manage your network, especially if you are more familiar with IP ranges or working with older systems that still use classful addressing.
The CIDR to IP range converter gives you all the key details you need for managing your network, including:
- ✓ Starting and ending IP addresses
- ✓ Netmask and binary netmask
- ✓ Total and usable IPs in the range
- ✓ Broadcast and wildcard mask
- ✓ Country and country code
- ✓ IP address class
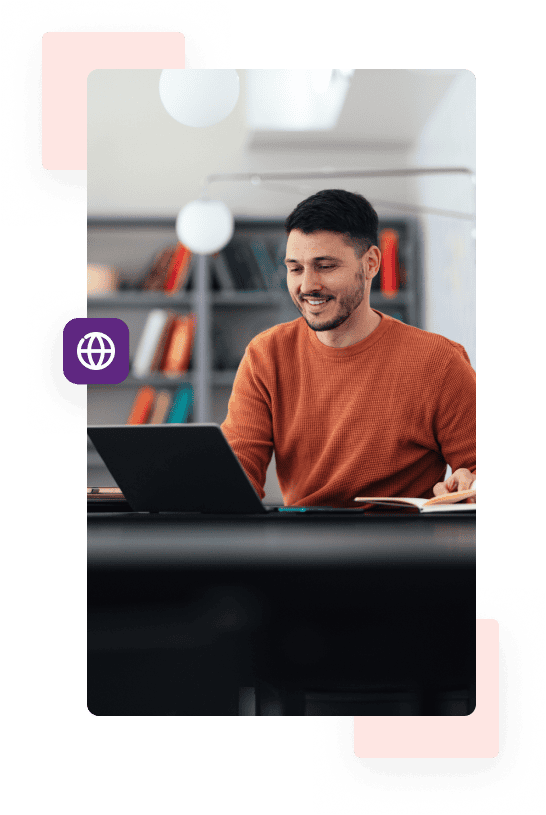


When to Use CIDR to IP Range Conversion
1. Network Setup & Management
Many network admins find IP ranges easier to work with than CIDR, especially if they're used to classful addressing (an older method still used in some setups). Being able to quickly convert CIDR to IP range makes managing and configuring networks much easier in these cases.
2. Email Server Configuration
Your email team or postmaster might be using servers that route traffic based on IP ranges instead of CIDR. Converting CIDR to a full IP range helps set up and manage these email servers properly.
Note: Classful addressing is mostly outdated. CIDR (classless addressing) is more flexible and helps save IPv4 addresses.
Monitor IPv4 Addresses and Improve Email Deliverability
Our free CIDR to IP range converter makes it easy to switch between CIDR and IP ranges. But great email deliverability takes more than just the right IP setup.
With FareOf’s email deliverability tools, both server admins and marketers get everything they need to send emails that land in the inbox.
Sign up for free and receive instant access to powerful tools designed for success.
What You Get with Your Free FareOf Account
100 free credits, no expiration
Email validation: Spot over 30 types of risky emails like invalid, disposable, spam traps, abuse emails, and more.
Catch-All Scoring: See which catch-all inboxes are actually being monitored.
Activity tracking: Check subscriber activity across the last 30, 60, 90, 180, 365+ days.
Email server testing*
Run 100+ checks including:
- Header and DNS testing
- Port checks
- DMARC analysis
Inbox placement testing*
Test emails with over 20 major providers:
- Google, Yahoo, Outlook, Comcast, iCloud, and more
- Plus filters like Spamhaus, Kaspersky, and Symantec
Email Finder*
Look up emails using names or domains
Blacklist Monitor*
Track your domain, subdomain, and both IPv4/IPv6 addresses
Powerful API access
- Use multiple API keys
- Connect with 60+ tools
- Full documentation
- Works on desktop or iOS
Trusted by 4,00,000 clients







FAQs
A CIDR to IP range converter quickly converts a CIDR block notation into an IP range that includes a starting and ending IP address. The converter also gives other useful information, such as the total number of usable IP addresses in the range and the class type.
CIDR sends data to IP addresses using a subnet mask or IP prefix, instead of relying on old IP classes.
An IP range (classful addressing) uses fixed groups called classes (like Class A, B, or C). While, CIDR doesn’t use classes. Instead, it defines the size of the network using a subnet mask, making it more flexible and efficient.
Classful addressing is a largely defunct method of inter-domain routing that offers no significant advantages over classless routing. However, some network managers continue to work with classful designs or ideas based on them.
Classful IP routing is based on five predefined classes, with no room for departure. As a result, many IP addresses are squandered when there are already fewer IPv4 addresses available. Classless addressing, often known as CIDR notation, addresses this issue by routing based on the subnet mask rather than the class.
Track your IPs and improve email delivery
Begin with a free trialReceive 100 email validation credits right away



